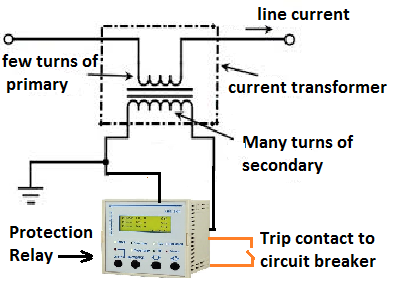
Protection special class CT 'PS" or 'PX' is used for protection of the electrical equipment like motor, transformer, generator, and bus bar. The protection or P class current transformer is used for the protection of feeders.
The central theme of any electrical protection scheme is that the current should not saturate at the time when fault current flows through the current transformer. Under CT saturation conditions, it behaves as an open circuit, and protection of the electrical equipment is not guaranteed.The protection class or 'P' class CT like 5P10, 5P20 is used for the protection of feeders. The knee point voltage of protection class CT is more than the knee point voltage of the metering class CT. It means the protection class CT saturates at much higher CT secondary voltage.
For the protection of the alternator, generator, high tension motor and bus bar, protection zone, differential protection, or unit protection scheme is used. The unit protection scheme provides tripping to the breaker in case there is a fault within the equipment. For instance, the differential protection trip in the transformer feeder shows that there is a fault in the transformer. If the differential protection relay operates, it is essential to check the transformer before switching on the equipment again.
The differential protection scheme is designed by selecting the PS class CT. The PS class CT has a higher knee point voltage. The following parameters of the current transformer of CT used for the PS class must be defined.
- Knee Point Voltage Vk(KPV) Minimum - Volts
- Excitation Current(Maximum) at Vk/2 - Amperes
- Rct (secondary winding resistance) at 75 Degree Centigrade (In Ohm)