DC Machine
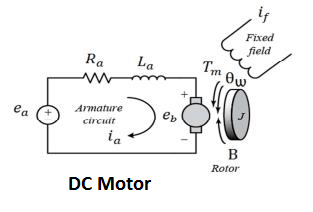
A DC Machine converts electrical energy into mechanical energy or mechanical energy into electrical energy. The DC motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy , and the DC generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
DC motor is widely used in the industrial applications where high starting torque and good speed regulation is desired. The DC motor has better speed regulation and high starting torque in comparison with the AC motor.
The construction of the DC motor and generator is almost similar. The generator is generally housed in the closed room and generator may be of open construction type. However, the DC motor is used at the site in the plant which may have dust and heat. Therefore, the DC motor enclosure is dust proof , fire proof, as per the applications.
The DC generator is used for the application where large DC power is required. The applications are electrolysis, electroplating etc.
Construction of Electrical DC Machines
The DC motor and DC generator have mainly two parts; stator and rotor. In dc motor stator is the stationary part and the rotor is rotating part. The rotor rotates in the air gap.The field winding is housed in the stator slots. The field winding produces the required magnetic field for motor operation. The armature winding is housed in the rotor. When DC voltage is fed to armature winding under magnetic field produced by field winding induce the voltage in the armature winding.
The small rating DC generator has field winding or permanent magnet on stationary part and voltage is taken out from the rotating part. In a large rating DC generator the field coils are housed on the rotor and the armature winding is housed in the stator part.